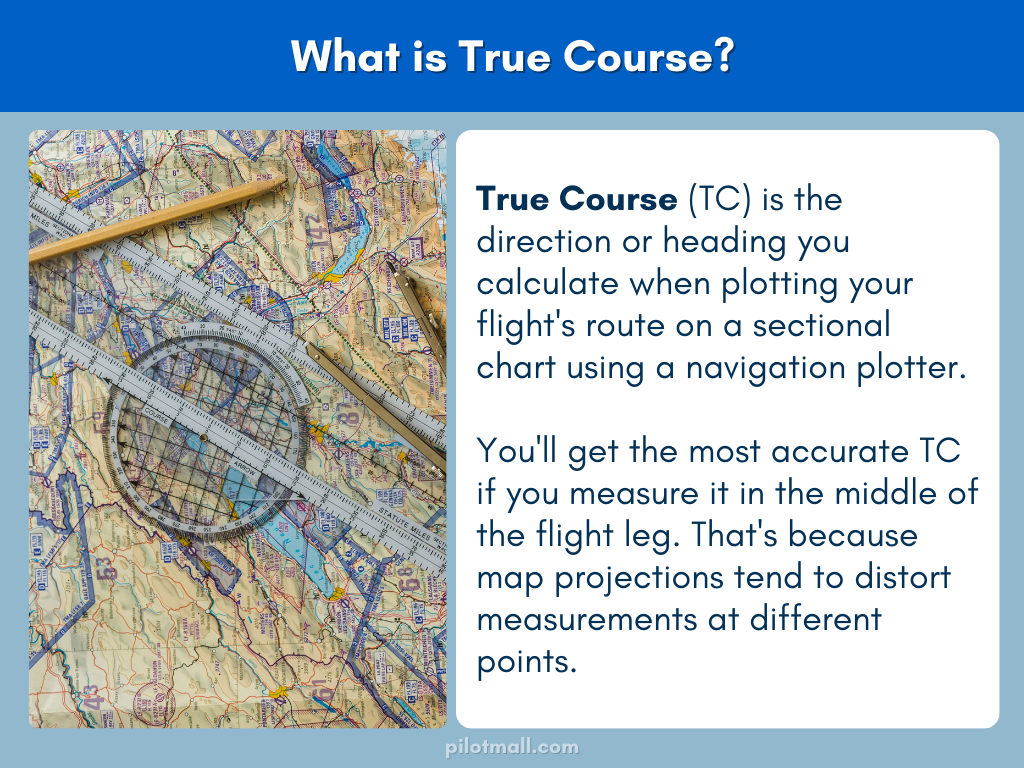
What Is Magnetic Course
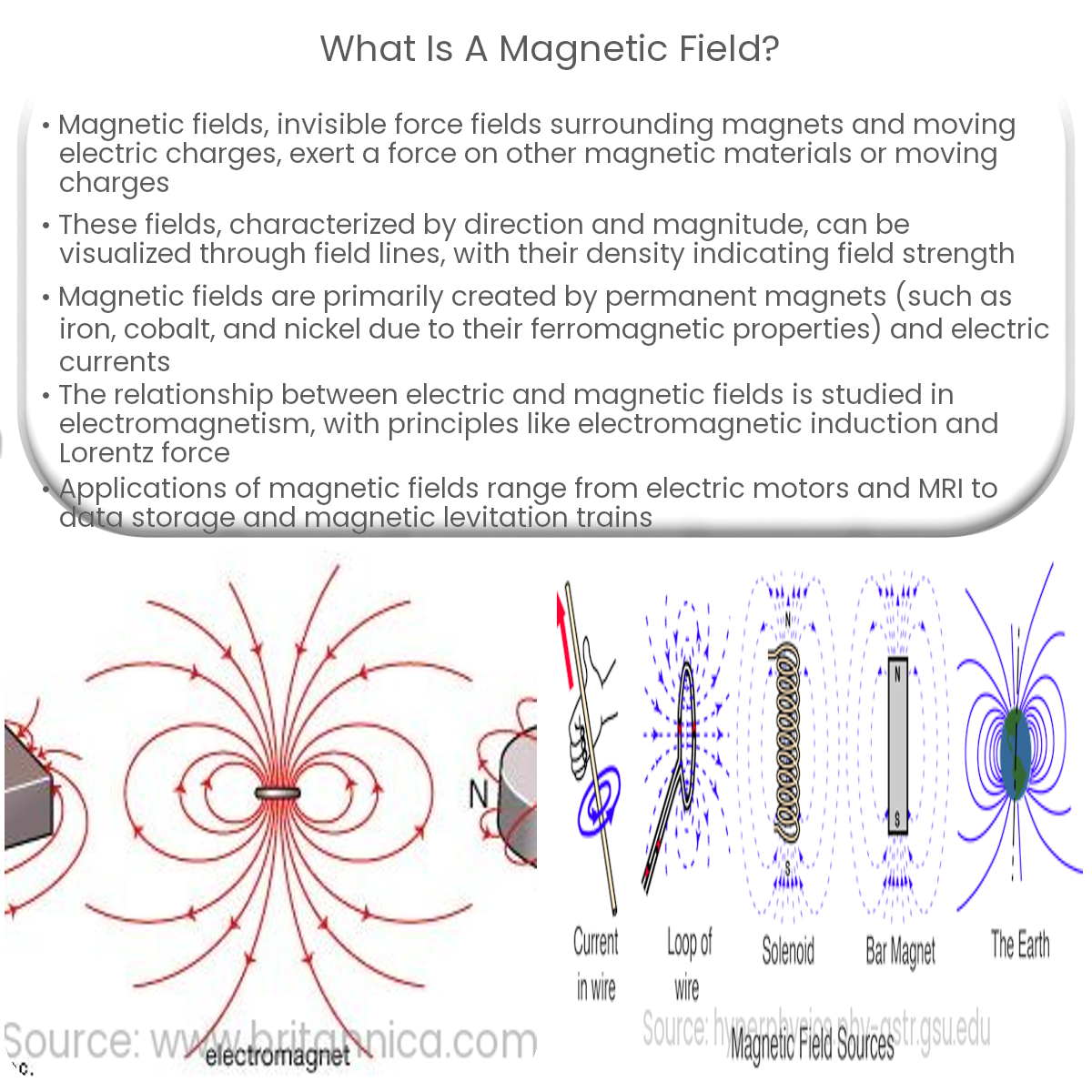
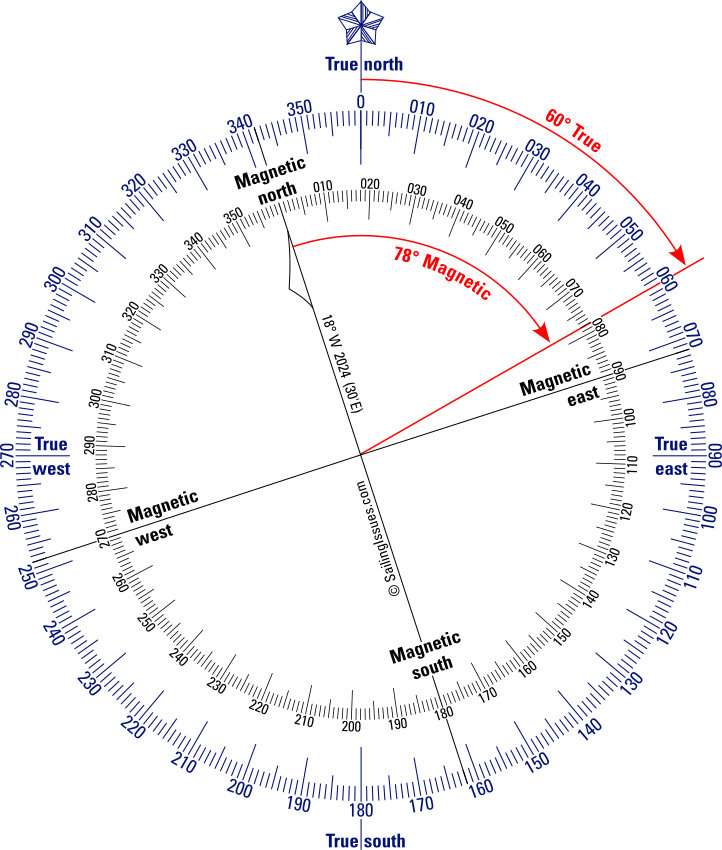
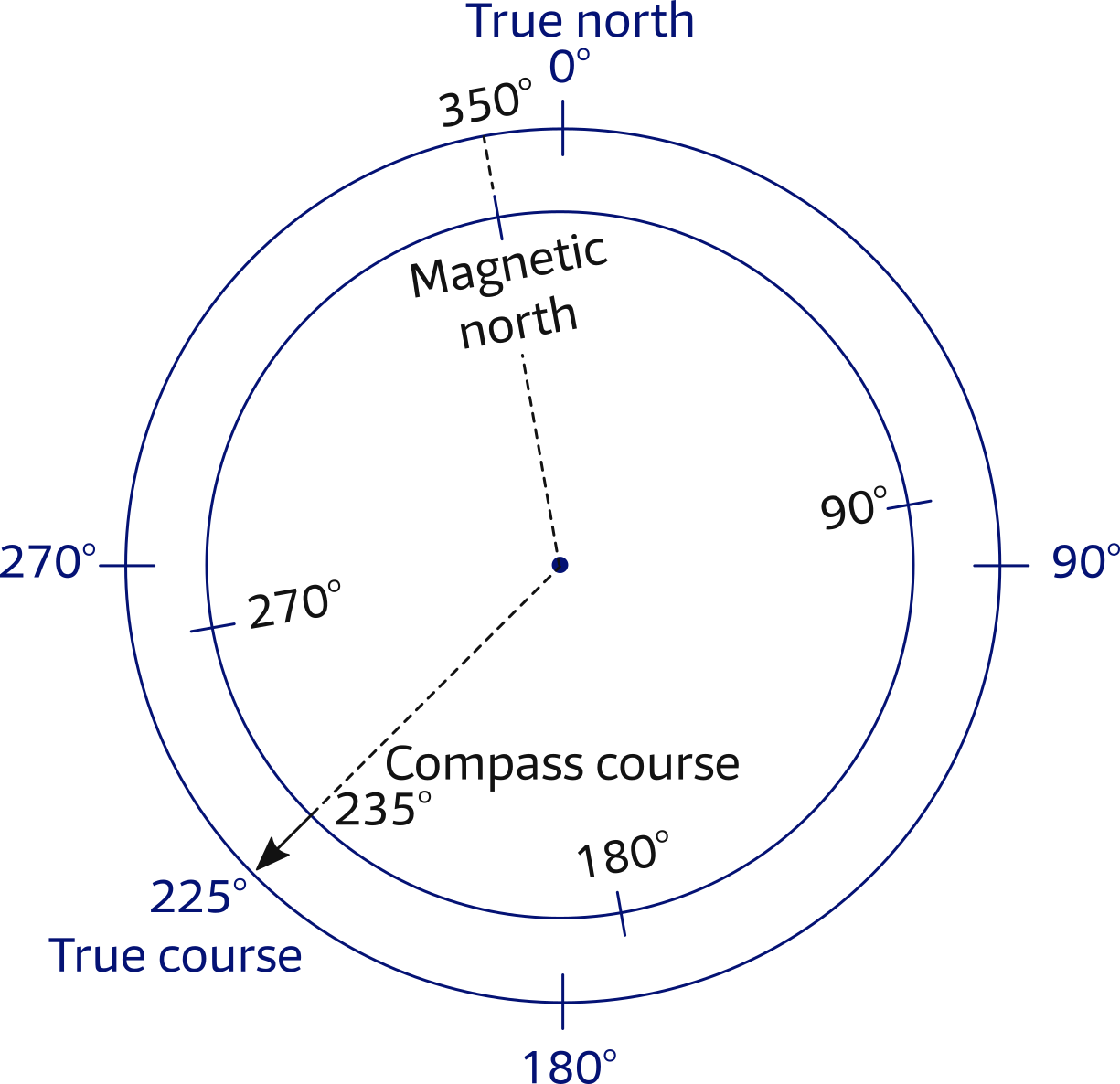
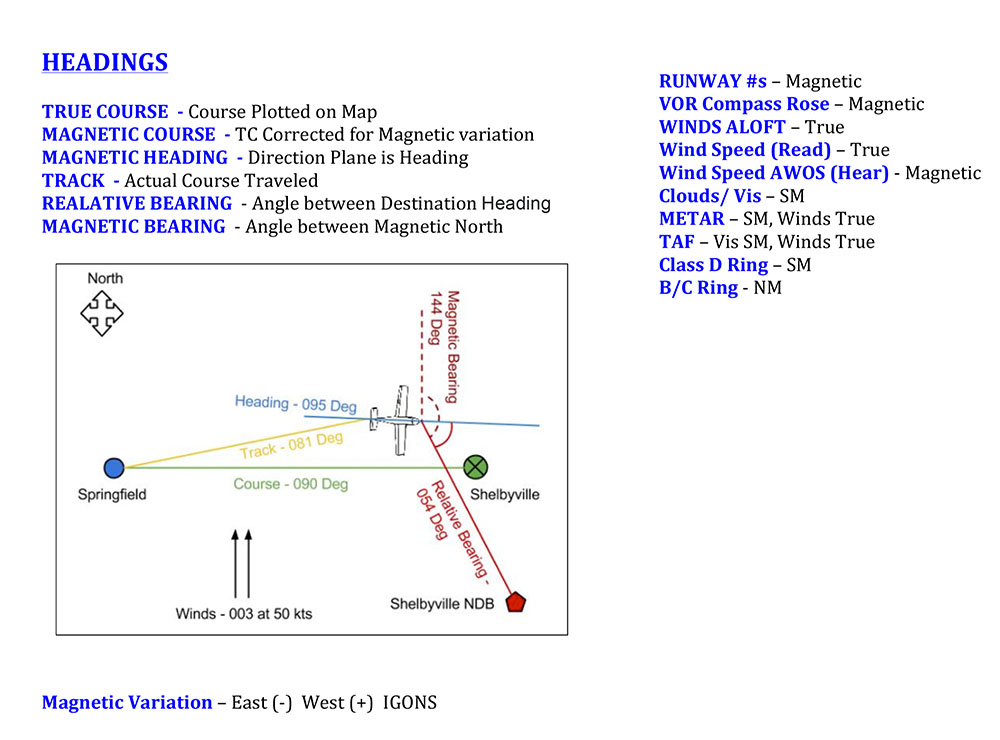
What Is Magnetic Course - A true heading is the course corrected for. The fundamental principle behind magnetism is the magnetic field, which arises from the motion of electric charges.this field exerts forces on other magnetic objects and. What is true course vs. The topographic information, upon which the course line is drawn, is oriented to true north, while the navigation information, which you need to get from airport to airport, is. Magnetic course (mc) refers to the intended path or route that a vessel or aircraft aims to follow over the earth’s surface, expressed in degrees from magnetic north. Bearing is the angle between any two. Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. This means that we are dealing. This is the planned path or track over the. Learn how magnetic fields influence navigation and the differences between. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading. Magnetic course, also called magnetic bearing, refers to the magnetic poles. Magnetic course (mc) is the direction over the ground that an aircraft intends to travel, measured clockwise from magnetic north. What is true course vs. Magnetic course (mc), is the true course (tc) adjusted for magnetic variation. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. The magnetic course (mc) is the course after magnetic variation has been considered, but without compensation for magnetic deviation. Heading is the direction the airplane is pointed, whereas track is the actual direction of the airplane tracking across the ground. Discover what the term 'magnetic course' means, its importance in navigation, usage, and related terminology. Magnetic course (mc) refers to the intended path or route that a vessel or aircraft aims to follow over the earth’s surface, expressed in degrees from magnetic north. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. Course, true course, magnetic course y desired track. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. This is the planned path. The fundamental principle behind magnetism is the magnetic field, which arises from the motion of electric charges.this field exerts forces on other magnetic objects and. This is the planned path or track over the. The meaning of magnetic course is the course on which an airplane is intended to be flown that is measured from magnetic north and that is. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. Further, on the typical paper vfr navigation plans it goes something akin to: This means that we are dealing. The fundamental principle behind magnetism is the magnetic. Bearing is the angle between any two. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. The fundamental principle behind magnetism is the magnetic field, which arises from the motion of electric charges.this field exerts forces. Further, on the typical paper vfr navigation plans it goes something akin to: Course, true course, magnetic course y desired track. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading. True heading is your direction relative to true north, or the geographic north pole. The magnetic course (mc) is the course after magnetic. The angle between magnetic course and true course is called magnetic variation. The fundamental principle behind magnetism is the magnetic field, which arises from the motion of electric charges.this field exerts forces on other magnetic objects and. A true heading is the course corrected for. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. Magnetic. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. Magnetic course (mc), is the true course (tc) adjusted for magnetic variation. Bearing is the angle between any two. Learn how magnetic fields influence navigation and the. This video explains how direction is measured on earth and the concepts of true course (tc), magnetic variation and magnetic course (mc) with graphical examp. Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative to magnetic north. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading. Magnetic course (mc) is the direction. This means that we are dealing. Magnetic heading is where the airplane is pointed. Course, true course, magnetic course y desired track. Magnetic course (mc) refers to the intended path or route that a vessel or aircraft aims to follow over the earth’s surface, expressed in degrees from magnetic north. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read. Learn how magnetic fields influence navigation and the differences between. Discover what the term 'magnetic course' means, its importance in navigation, usage, and related terminology. The angle between magnetic course and true course is called magnetic variation. Further, on the typical paper vfr navigation plans it goes something akin to: Magnetic course is the airplane’s course across the ground, relative. This means that we are dealing. Magnetic heading is your direction relative to magnetic north, read from your magnetic compass. Learn how magnetic fields influence navigation and the differences between. This is the planned path or track over the. The meaning of magnetic course is the course on which an airplane is intended to be flown that is measured from magnetic north and that is the true course as laid out on the chart. This video explains how direction is measured on earth and the concepts of true course (tc), magnetic variation and magnetic course (mc) with graphical examp. Course, true course, magnetic course y desired track. Bearing is the angle between any two. What is true course vs. Magnetic course (mc), is the true course (tc) adjusted for magnetic variation. The topographic information, upon which the course line is drawn, is oriented to true north, while the navigation information, which you need to get from airport to airport, is. A true heading is the course corrected for. A magnetic field is the region around a magnet where a force acts on another magnet or on a magnetic material close magnetic materiala material that is attracted to a magnet, such as. Magnetic heading is where the airplane is pointed. This means that we are dealing with the rewritten. In this article we discuss navigation concepts and look at the differences between course and heading.¿Qué es un campo magnético?
What is Field? YouTube
Marine navigation courses compass ASA RYA
Marine navigation courses compass ASA RYA
Aviation Heading Chart at Lee Porter blog
True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
PPT Chapter 6 Approach Charts PowerPoint Presentation, free download
True Course vs True Heading vs (How Are They Different?)
True and Course Courses and Headings in Navigation (Part 1/2
Plato.is / Navigation / Navigation Courses Course
Magnetic Course (Mc) Refers To The Intended Path Or Route That A Vessel Or Aircraft Aims To Follow Over The Earth’s Surface, Expressed In Degrees From Magnetic North.
Magnetic Course Is The Course That Would Take You Directly From Origin To Destination If There.
A True Course Is A Heading Based On The Direction You Intend To Travel.
Magnetic Course Is The Airplane’s Course Across The Ground, Relative To Magnetic North.
Related Post: